X-Rings and Quad-Ring® Seals
 November 06, 2024
November 06, 2024
|
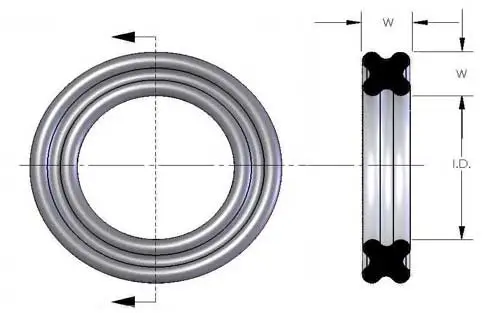
X-Rings, also known as Quad-Ring© Seals, can be used in a wide variety of static and dynamic sealing applications. In reciprocating applications, the X-Ring's four-lobed design prevents spiral failure and in rotary applications, it prevents the seal from bunching and failing. We supply both Quad-Ring© branded seals manufactured by Minnesota Rubber and Plastics, Quadion LLC, as well as similar seals described in various ways like X-Rings and Q-Rings. |
The four-lobed design provides two sealing surfaces compared to a standard O-ring. This reduction in force means less friction and improved seal life.
X-Ring parting lines are between the lobes, away from the sealing surface, thus eliminating the problems of leakage often resulting from a parting line's irregular surface as found on an O-Ring. The unique design of the X-Ring allows it to be used in narrower grooves and also in standard width O-ring grooves.
Features
- Recommended for low speed reciprocating or oscillatory motion if O-Rings twist.
- Provides lower friction than O-Rings and Square Rings.
- X-Rings are interchangeable with O-Ring sizes and gland design.
- Available in standard and custom sizes like O-Rings.
- Readily available in USA AS568 standard sized NBR Buna-N and FKM.
- Not recommended for pressures >500 psi.
- Custom size X-Rings may require tooling costs in some compounds.
Enhanced Sealing Solutions for Dynamic and Static Applications
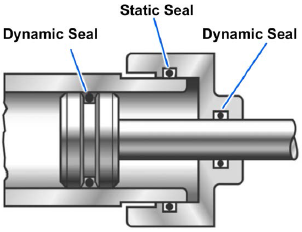
The X-Ring, also known as the Quad-Ring© Seal, represents a modern solution to a wide range of sealing challenges. This design gives X-Rings specific advantages in both static and dynamic seal applications. Whether the movements are reciprocating, oscillating, or rotary, X-Rings reduce common seal failures and extend operational life. Herein, we will explore in detail the design, advantages, limitations, and applications of X-Rings.
Why X-Rings?
The distinctive four-lobed design of the X-Ring allows for a double-seal action, providing two sealing surfaces rather than one, as would be the case with a conventional O-ring. The design, therefore, requires less force to achieve a tight seal, hence minimizing friction and improving operational seal life. As friction is reduced and wear minimized, X-Rings are the ideal application when durability and performance are critical.
Other design advantages are that the parting lines—the lines that result from manufacturing—are between the lobes and away from the sealing surfaces. This eliminates one of the most common failure modes associated with conventional O-rings, which involve leaks from irregularities in the parting lines. Furthermore, the X-Rings can operate in much narrower grooves, allowing for a wide range of applications and specific sealing requirements but still accommodating standard O-ring grooves.
Key Advantages of X-Rings
Less friction and wear:
Because of design, X-Rings support pressure more evenly and create less friction compared to other seals, like O-rings or square rings. This is very appropriate for low-speed applications—essentially reciprocating or oscillating—where ordinary O-rings would otherwise twist or roll.Better Leak Prevention:
The double-seal effect of X-Rings creates a more secure seal with less deformation, which makes fewer leaks and enhances performance over long periods.- X-Rings come in the same sizes as standard O-ring sizes. Because they are available in similar sizes, they can be used directly in existing O-ring glands and grooves, directly replacing standard O-rings. This makes interchangeability easy and retrofitting and design modification less hassle.
Material Variety:
The X-Ring is made from several different materials, each suited for a specific environmental application. Nitrile [NBR] would be a standard choice for general service sealing; FKM [Viton®] would provide compatibility in most chemical services. Special compounds are available for extreme temperatures, or where special chemical compatibility may be required.Wide Operating Temperature Range:
Depending on the material of its construction, X-Rings can operate over a wide operating temperature range, from as low as -40°C to as high as 200°C with some compounds.
.webp)
Considerations and Limitations
Although X-Rings are quite versatile, they do have some limitations:
Constraints of Pressure:
As a whole, there is not a recommendation for using X-Rings in applications above 500 psi. Alternative choices in sealing should be considered to avoid performance issues in such cases.Compatibility of Compound:
Not all compounds work with an X-Ring, so confirmation should be considered when compatibility is in question with specific materials, particularly in critical applications. Some compounds may utilize only custom-sized X-Rings, involving tooling costs.
Typical Applications of X-Rings
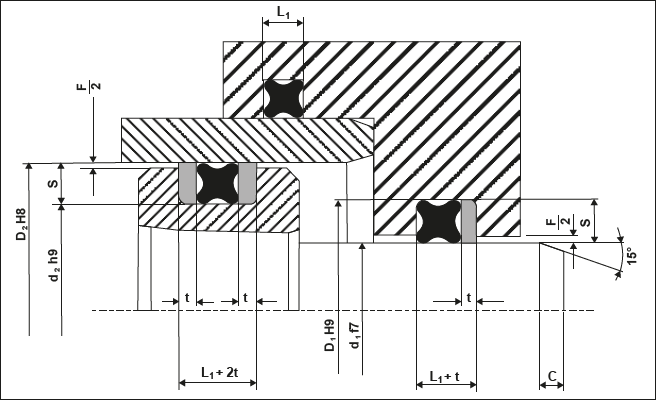
X-Rings find broad applications in many industries due to their versatility and strong sealing force. Typical uses include:
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems:
X-Rings are fitted for hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic actuators, and similar equipment, which require dependable seals that reduce friction and allow less leakage.Automotive:
Transmission and fuel systems use X-Rings as does the sealing systems of engines, bearing continuous vibration, temperature fluctuation, and action of liquids.Medical Devices:
Medical applications with fluid transport, and even drug delivery devices like syringes, depend on reliable seals with low friction provided by X-Rings. Leak-resistant, these designs form the backbone of applications where precision and reliability are so vital.Aerospace:
Aerospace demands of pressure compatibility and sealing applications benefit from X-Rings as well as their versatility for harsh environmental compatibility.
Conclusion
The X-Ring represents an advanced design in sealing solutions that bridges gaps left by traditional seals such as O-Rings. With their double-seal action, reduced friction, increased versatility in fitment and enhanced durability, X-Rings can be an essential solution for dynamic and static applications across various industries. Seals are among the simplest yet most crucial of parts in machinery, and selecting the right seal can save on costs, enhance safety, and extend the lifecycle of systems.

X-Rings, also known as Quad-Ring© Seals, can be used in a wide variety of static and dynamic sealing applications. In reciprocating applications, the X-Ring's four-lobed design prevents spiral failure and in rotary applications, it prevents the seal from bunching and failing. We supply both Quad-Ring© branded seals manufactured by Minnesota Rubber and Plastics, Quadion LLC, as well as similar seals described in various ways like X-Rings and Q-Rings.
The four-lobed design provides two sealing surfaces compared to a standard O-ring. This reduction in force means less friction and improved seal life.
X-Ring parting lines are between the lobes, away from the sealing surface, thus eliminating the problems of leakage often resulting from a parting line's irregular surface as found on an O-Ring. The unique design of the X-Ring allows it to be used in narrower grooves and also in standard width O-ring grooves.
Features
- Recommended for low speed reciprocating or oscillatory motion if O-Rings twist.
- Provides lower friction than O-Rings and Square Rings.
- X-Rings are interchangeable with O-Ring sizes and gland design.
- Available in standard and custom sizes like O-Rings.
- Readily available in USA AS568 standard sized NBR Buna-N and FKM.
- Not recommended for pressures >500 psi.
- Custom size X-Rings may require tooling costs in some compounds.
Enhanced Sealing Solutions for Dynamic and Static Applications

The X-Ring, also known as the Quad-Ring© Seal, represents a modern solution to a wide range of sealing challenges. This design gives X-Rings specific advantages in both static and dynamic seal applications. Whether the movements are reciprocating, oscillating, or rotary, X-Rings reduce common seal failures and extend operational life. Herein, we will explore in detail the design, advantages, limitations, and applications of X-Rings.
Why X-Rings?
The distinctive four-lobed design of the X-Ring allows for a double-seal action, providing two sealing surfaces rather than one, as would be the case with a conventional O-ring. The design, therefore, requires less force to achieve a tight seal, hence minimizing friction and improving operational seal life. As friction is reduced and wear minimized, X-Rings are the ideal application when durability and performance are critical.
Other design advantages are that the parting lines—the lines that result from manufacturing—are between the lobes and away from the sealing surfaces. This eliminates one of the most common failure modes associated with conventional O-rings, which involve leaks from irregularities in the parting lines. Furthermore, the X-Rings can operate in much narrower grooves, allowing for a wide range of applications and specific sealing requirements but still accommodating standard O-ring grooves.
Key Advantages of X-Rings
Less friction and wear:
Because of design, X-Rings support pressure more evenly and create less friction compared to other seals, like O-rings or square rings. This is very appropriate for low-speed applications—essentially reciprocating or oscillating—where ordinary O-rings would otherwise twist or roll.Better Leak Prevention:
The double-seal effect of X-Rings creates a more secure seal with less deformation, which makes fewer leaks and enhances performance over long periods.- X-Rings come in the same sizes as standard O-ring sizes. Because they are available in similar sizes, they can be used directly in existing O-ring glands and grooves, directly replacing standard O-rings. This makes interchangeability easy and retrofitting and design modification less hassle.
Material Variety:
The X-Ring is made from several different materials, each suited for a specific environmental application. Nitrile [NBR] would be a standard choice for general service sealing; FKM [Viton®] would provide compatibility in most chemical services. Special compounds are available for extreme temperatures, or where special chemical compatibility may be required.Wide Operating Temperature Range:
Depending on the material of its construction, X-Rings can operate over a wide operating temperature range, from as low as -40°C to as high as 200°C with some compounds.
.webp)
Considerations and Limitations
Although X-Rings are quite versatile, they do have some limitations:
Constraints of Pressure:
As a whole, there is not a recommendation for using X-Rings in applications above 500 psi. Alternative choices in sealing should be considered to avoid performance issues in such cases.Compatibility of Compound:
Not all compounds work with an X-Ring, so confirmation should be considered when compatibility is in question with specific materials, particularly in critical applications. Some compounds may utilize only custom-sized X-Rings, involving tooling costs.
Typical Applications of X-Rings

X-Rings find broad applications in many industries due to their versatility and strong sealing force. Typical uses include:
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems:
X-Rings are fitted for hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic actuators, and similar equipment, which require dependable seals that reduce friction and allow less leakage.Automotive:
Transmission and fuel systems use X-Rings as does the sealing systems of engines, bearing continuous vibration, temperature fluctuation, and action of liquids.Medical Devices:
Medical applications with fluid transport, and even drug delivery devices like syringes, depend on reliable seals with low friction provided by X-Rings. Leak-resistant, these designs form the backbone of applications where precision and reliability are so vital.Aerospace:
Aerospace demands of pressure compatibility and sealing applications benefit from X-Rings as well as their versatility for harsh environmental compatibility.
Conclusion
The X-Ring represents an advanced design in sealing solutions that bridges gaps left by traditional seals such as O-Rings. With their double-seal action, reduced friction, increased versatility in fitment and enhanced durability, X-Rings can be an essential solution for dynamic and static applications across various industries. Seals are among the simplest yet most crucial of parts in machinery, and selecting the right seal can save on costs, enhance safety, and extend the lifecycle of systems.

